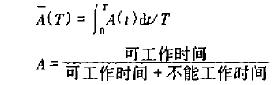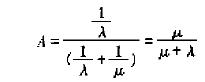Generalized Reliability Growth in CNC System Development
CNC systems are widely used in various types of electromechanical equipment. Due to the complexity of the CNC system and the importance of control, in general, its reliability requirements are high. High reliability is the guarantee of the application of advanced control methods. However, the reliability of any product has been raised to a certain degree, and it is very difficult to raise it again. Although it costs a lot, it has little effect. Because to this extent, the defects that can be eliminated have been eliminated, leaving only those defects that cannot be controlled or predicted. Failures caused by these defects are accidental failures. It is difficult to eliminate. 1 The concept of generalized reliability Generalized reliability is also called validity. For a repairable product, it is a combination of reliability and maintainability to evaluate the product. Generalized reliability is a measure of generalized reliability. Ability to maintain the probability of work. Expressed by A(t), it is a function of time. If A (300) = 0.96, it means that 100 devices have an average of 96 devices that can operate in the normal state within 300 hours of the specified working time. As for the number of failures during this period, it is irrelevant when they fail. As long as it is repaired within the stipulated time, it is guaranteed that 96 units will be satisfactory if they reach 300 hours. If a piece of equipment A = 0 96 means that the equipment is 96% of the time in the effective state, allowing the middle of a failed parking repair. This is different from R(300)=0 96. R(300)=0 96 indicates that the probability of a device operating normally for 300 hours is 96%. Generalized Reliability Commonly Used Instantaneous Validity A(1), Average Effectiveness For faults occurring accidentally faulty products, the faults are not constantly changed. The distribution of the faults when working without faults is generally described by an exponential distribution, that is, the fault rate λ is a constant. Similarly, the repair time of a product is often described by an exponential distribution, ie, the repair rate μ is a constant. In too many cases, the inability to work is the repair time. and so From this formula, we can see that reducing λ or increasing μ can increase the value of A. Therefore, the growth of the general reliability of the repairable system can be achieved by improving the reliability and by improving maintainability. 2 The general reliability of numerical control system increases The general reliability of numerical control systems has grown, and the reliability and maintainability growth must be considered comprehensively. Of course, the growth of reliability still needs to be given priority. Only when the cost for reliability growth exceeds the cost of maintenance and downtime savings due to reliability growth, and users have no special requirements, do not continue to pursue reliability growth. The next focus of work should shift to improving maintenance. In the development of CNC systems, measures that can reduce costs and even increase reliability or maintainability at no cost are of course the best; and measures that can simultaneously improve reliability and maintainability are also prioritized. 2.1 Measures to improve reliability and maintainability at the same time (1) To simplify the design as much as possible, that is, to make the circuit as simple as possible, the number of components, the number of varieties, and the degree of integration; (2) To achieve standardization, systematization, and generalization of components and components as much as possible; (3) CNC software adopts modular design as much as possible. 2.2 Measures to Improve Reliability and Reduce Costs Try to use software instead of hardware to achieve the desired functionality. The cost of software is relatively low, while the reliability is relatively high. When the operating speed requirement is not very high, the function of the software should be fully utilized. To reduce the number of components and improve the reliability of the system. 2.3 Common Measures for Reliability Growth of CNC Systems (1) Improve the reliability of weak links and adopt redundant designs at key locations; (2) Select the type of parts and reduce the load by using electrical devices to reduce the failure rate; (3) design circuit considers inheritance; (4) Consider the protection of transient current and voltage. Design a circuit that is insensitive to component parameter drift as much as possible; (5) Minimize the number of contacts and improve the quality of contacts. The plug of the printed board adopts double-sided connection; (6) Adopt hardware anti-jamming design. For example, isolation of power supply interference, photoelectric isolation of strong and weak currents, shielding of electromagnetic interference, etc. These measures are used to prevent software from being lost and changed, in order to improve the reliability of software operation; (7) Anti-jamming in software design, such as automatically removing the value of the over-limit; automatically removing illegal data to determine the well. For example, in the GICC system, the emergency stop function is set to improve reliability. In the event of an accident, pressing the STOP key will immediately stop the tool rest and display the word STOP in the upper right corner of the screen, taking into account the subsequent operation after the emergency stop. It can avoid too much trouble. 2.4 Common Measures to Improve Maintenance of CNC System (1) Simplify maintenance. Reduce the difficulty and complexity of maintenance; reduce the number and time of maintenance; reduce the number of maintenance personnel and requirements for maintenance equipment; use components with good interchangeability. (2) Improve fault detectability. Design a more centralized detection point that does not require disassembly to facilitate detection and fault location. (3) Accessibility design, making it easy to repair, update, and maintain faulty components or components. (4) Conduct maintenance safety design. Ensure the safety of maintenance operations; adopt a design that prevents maintenance personnel from wearing electric shocks; and add obvious warnings to areas that may be unsafe. (5) Design to improve maintenance efficiency. Use components or components that can be quickly assembled or disassembled; use proper structural design so that when a part is repaired, there is little or no need to disassemble other components or components. (6) Design for error prevention. Misconfigurations and misoperations may occur, so design should be avoided. (7) Conduct ergonomic design. Make sure there is sufficient maintenance space for maintenance, enough brightness, less vibration and noise. (8) Maintain maintainability of the software. To facilitate the recovery, modification of lost programs and data. (9) Carry out diagnostic design. Various diagnostic programs are set to prevent the occurrence and expansion of failures. After a fault occurs, the type and location of the fault can be quickly identified. (10) Design of monitoring functions. It can monitor the status of the CNC system and alarm the NC system to provide fault diagnosis information. For example, in the GICC system, a reset function is designed to improve maintainability. In the event of a fault shutdown due to an interrupted operating result caused by program and data processing, the reset button can be pressed to bring the control system into normal operation. Doing so will not undermine the software and normal processing results. 3 Conclusion The growth of generalized reliability in the development of numerical control systems is not only the increase of reliability but also the improvement of maintainability. The growth of generalized reliability should achieve its goal with the most economical means. Electric Power Fittings,Electrical Wiring Fittings,Electric Power Fitting,Home Electrical Wiring Fittings DONGYING SHENGYU METAL PRODUCT CO.,LTD , https://www.castingprocess.com
For most numerical control systems, although higher reliability is required, they are not completely unallowable. Therefore, they are all repairable systems. Since it is a repairable system. It is no longer practical to talk about the narrow sense of reliability of the system, but rather to consider generalized reliability including maintenance. 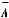 (T), time effectiveness A to indicate.
(T), time effectiveness A to indicate.