The encoding of the two main baseband signals is given below.
(1) In the level coding, binary values ​​respectively correspond to the high and low voltage levels of the signal level. For example, the non-return to zero (NRZ) code, which is one of the simplest encoding methods, has a logical high binary value of 1 and a logical low binary value of 0. In order to avoid a series of consecutive Signals caused by 0 or 1 are not synchronized and it is difficult to rebuild the time base. After each binary value, the signal will fall back to 0 volts. This encoding is return to zero (RZ). A positive pulse pair is used for a binary value of one, whose duration is equal to half the symbol time and in other cases it is a low logic level. In addition, the data is encoded. (NRZ or RZ) has nothing to do with previous data encoding.
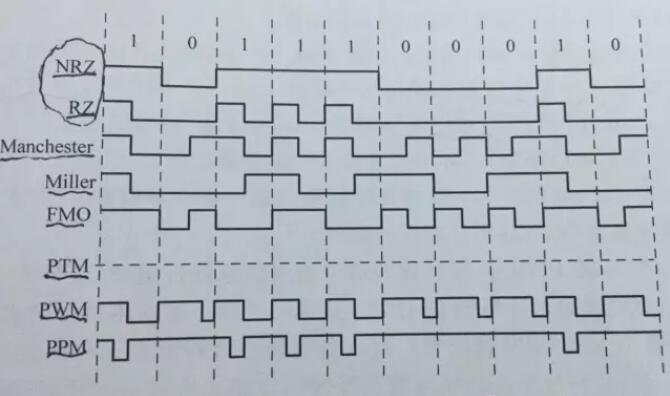
(2) In the coding of signal transitions, the binary digits correspond to the changes of the two voltage levels of the signal; the information is contained in the transition of the signal, and the encoding of the data is related to the preceding data encoding. Clock synchronization under this type of coding is easier than in level coding.
1 Manchester encoding is a type of signal FM encoding. He represents a binary value with the instantaneous value of each bit at the half-period edge, so the middle rising edge of the symbol time corresponds to the binary value 0, and the falling edge corresponds to the binary value 1. The bit rate is equal to the communication bandwidth. The middle transition of the symbol time is very important when receiving the synchronization signal, especially when a plurality of cards are within the operating range of the RFID reader. However, the Manchester code has a higher bandwidth than other encoding methods. In addition, the Manchester code ensures that the data encoding is independent of the encoding of previous data during encoding.
The 2 Miller code is another type of transition code that encodes the binary value 1 using a symbolic time intermediate transition. If there are consecutive 0-bits, a transition is added at the beginning of the symbol time, which ensures that there is a logic level change after at least two symbol time periods. The other is known as the “Supplementer Miller Code,†which is a variant of the Miller code, which has the same principle as the Miller code, but replaces each jump with a negative pulse. The bandwidth required for the transmission of this type of code is lower than the previous one. Kinds of coding should be wide. The encoding of previous data must be considered in Miller coding.
3 Biphase Interleaved code Similar to the Miller code, it performs phase reversal at the beginning of each symbol time period, indicating 1 . If the level also has a phase reversal in the middle of the symbol time in addition to the reversal at the beginning of the period, 0 is represented. Compared with the Miller code, this encoding mechanism can better synchronize the encoded data when receiving the signal. The FM0 code is similar to the Miller code, and the previous coded data must also be considered.
Other encoding methods transmit information by pulse-time modulation. In this type of coding, pulse width modulation, pulse position modulation and pulse interval coding are generally used.
(1) Pulse width modulation (PWM). The pulses are regularly spaced with equal amplitude signals and their length is proportional to the signal period. The PWM code associates the binary value with the positive pulse length. At the end of the symbol time, the level usually goes back to low, then to the high point, and then starts a new code.
(2) Pulse Position Modulation (PPM). The information is encoded according to the position of the pulse. The PPM code uses a negative pulse to encode a logic one. Unlike the modified Miller code, a continuous logic zero is usually encoded with a constant high level. Correspondingly, an n-th order ppm code can be used to encode n-bit logic words. The position of the pulse in the time period determines the code word. However, any word must be encoded by the position of the negative pulse: It is impossible to find a constant level throughout the symbol time. Compared with the Manchester Chester horse code, the bandwidth of this encoding method is relatively narrow and easy to implement, but the data rate of this encoding method is low.
(3) Pulse interval coding (PIE). It is a variant of PPM modulation in which the reader generates two falling edges to determine the interval of pulses, which is a function of the binary numbers 0 and 1.
The encoding technology of RFID information must consider the following constraints:
1. The code must save energy transmission as long as possible.
2, encoding can not consume too much bandwidth.
3. If there are several RFID tags at the same time within the operating range of the reader, the code should be able to have a conflict of interest test.
Since PPM, PIE, and PWM coding have relatively stable signals, the first two constraints can be satisfied. However, it should also be noted that the Manchester code can be more easily detected as a collision, so this encoding is usually used in the return link where the RFID tag sends data to the reader.
The NRZ code and the Miller code have the lowest coding bandwidth, and their bandwidth is only half of the data bit rate bandwidth. Followed by Manchester encoding, FM0 code and RZ code, their bandwidth and traffic are the same.
The choice of representing the binary code needs to consider the remote power supply problem. The carrier signal must satisfy the long-distance power supply needs as long as possible. At this time, NRZ or Lema code can be used. Considering the data interaction between the iRFID tag and the reader, it is important to detect the response contained in the feedback signal. Encoding can be simplified by letting the Manchester code, etc., have a transition in the symbol period.
Copper Pipe
Copper pipe is also known as copper pipe. A non-ferrous metal tube is a pressed and drawn seamless tube. Copper pipe has good electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity characteristics, electronic products of conductive parts and heat dissipation parts of the main material, and has become a modern contractor in all residential commercial housing water pipeline, heating, cooling pipe installation of the first choice. Copper pipe corrosion resistance is strong, not easy to oxidation, and some liquid substances are not easy to react chemically, easy to Wei bending shape.
Copper pipe (also known as red copper pipe), often used in water pipes, heating and cooling pipes, can be used in different environments. Copper pipe set the advantages of metal and non-metal pipe in a body, in the hot and cold water system exclusive torture, is the best connection pipe. Copper pipes are refractory and heat-resistant, and can maintain their shape and strength at high temperature without aging.
The pressure resistance of copper pipe is several times or even dozens of times that of plastic pipe and aluminum plastic pipe, and it can withstand the highest water pressure in today's buildings. In the hot water environment, with the extension of service life, the bearing capacity of plastic pipe significantly decreases, while the mechanical properties of copper pipe remain unchanged in all thermal temperature ranges, so its pressure resistance will not be reduced, nor will aging occur.
The linear expansion coefficient of copper pipe is very small, is 1/10 of plastic pipe, will not cause stress fatigue rupture because of excessive thermal expansion and cold contraction.
The strength of copper pipe is greater, and the outside diameter is smaller to ensure the effective inside diameter, which is more suitable for hidden burial.
